First-class citizen(일급 객체)
- Function (함수)
- can assign into variable
- can refer to argument(인자) of other function
- can return as the result of other function
- function expression(함수 표현식)
- can not use before assignment(할당)
- hoisting is not happening unlike 'function declaration'(함수 선언식)
Higher order function(고차 함수)
함수 = 값을 전달 받아 값을 리턴한다 = 값에 대한 복잡한 로직은 감추어져 있다 = 값 수준에서의 추상화
값 수준의 추상화: 단순히 값(value)을 전달 받아 처리하는 수준
사고의 추상화: 함수(사고의 묶음)를 전달 받아 처리하는 수준
고차함수 = 함수를 전달 받거나 함수를 리턴한다 = 사고(함수)에 대한 복잡한 로직은 감추어져 있다 = 사고 수준에서의 추상화
- a function that takes as a argument or returns a function
- Callback function
- a function passed into caller(another function) as an argument, which is then invoked(호출)
- depends on caller's condition, can decide callback function to be executed or executed even several times
- mostly invoked when certain work is done so called as callback
- Curry function
- specifically for a function that returns function
- part of higher order function
- When it takes caller(other function) as an argument
1234567891011121314function triple(num) {return num * 3;}function doubleNum(func, num) {return func(num);}// 함수 doubleNum은 다른 함수를 인자로 받는 고차 함수입니다.// 함수 doubleNum의 첫 번째 인자 func에 함수가 들어올 경우// 함수 func는 함수 doubleNum의 콜백 함수입니다.// 아래와 같은 경우, 함수 double은 함수 doubleNum의 콜백 함수입니다.let output = doubleNum(triple, 4);console.log(output); // -> 12
cs - When it returns function
12345678910111213141516171819function adder(added) {return function (num) {return num + added;};}// 함수 adder는 다른 함수를 리턴하는 고차 함수입니다.// adder는 인자 한 개를 입력받아서 함수(익명 함수)를 리턴합니다.// 리턴되는 익명 함수는 인자 한 개를 받아서 added와 더한 값을 리턴합니다.// adder(5)는 함수이므로 함수 호출 연산자 '()'를 사용할 수 있습니다.let output = adder(5)(3); // -> 8console.log(output); // -> 8// adder가 리턴하는 함수를 변수에 저장할 수 있습니다.// javascript에서 함수는 일급 객체이기 때문입니다.const add3 = adder(3);output = add3(2);console.log(output); // -> 5
cs - When it takes function as argument and returns function
123456789101112131415161718192021function double(num) {return num * 2;}function doubleAdder(added, func) {const doubled = func(added);return function (num) {return num + doubled;};}// 함수 doubleAdder는 고차 함수입니다.// 함수 doubleAdder의 인자 func는 함수 doubleAdder의 콜백 함수 입니다.// 함수 double은 함수 doubleAdder의 콜백으로 전달되었습니다.// doubleAdder(5, double)는 함수이므로 함수 호출 기호 '()'를 사용할 수 있습니다.doubleAdder(5, double)(3); // -> 13// doubleAdder가 리턴하는 함수를 변수에 저장할 수 있습니다. (일급 객체)const addTwice3 = doubleAdder(3, double);addTwice3(2); // --> 8
cs
Built-in higher order functions(내장 고차 함수)
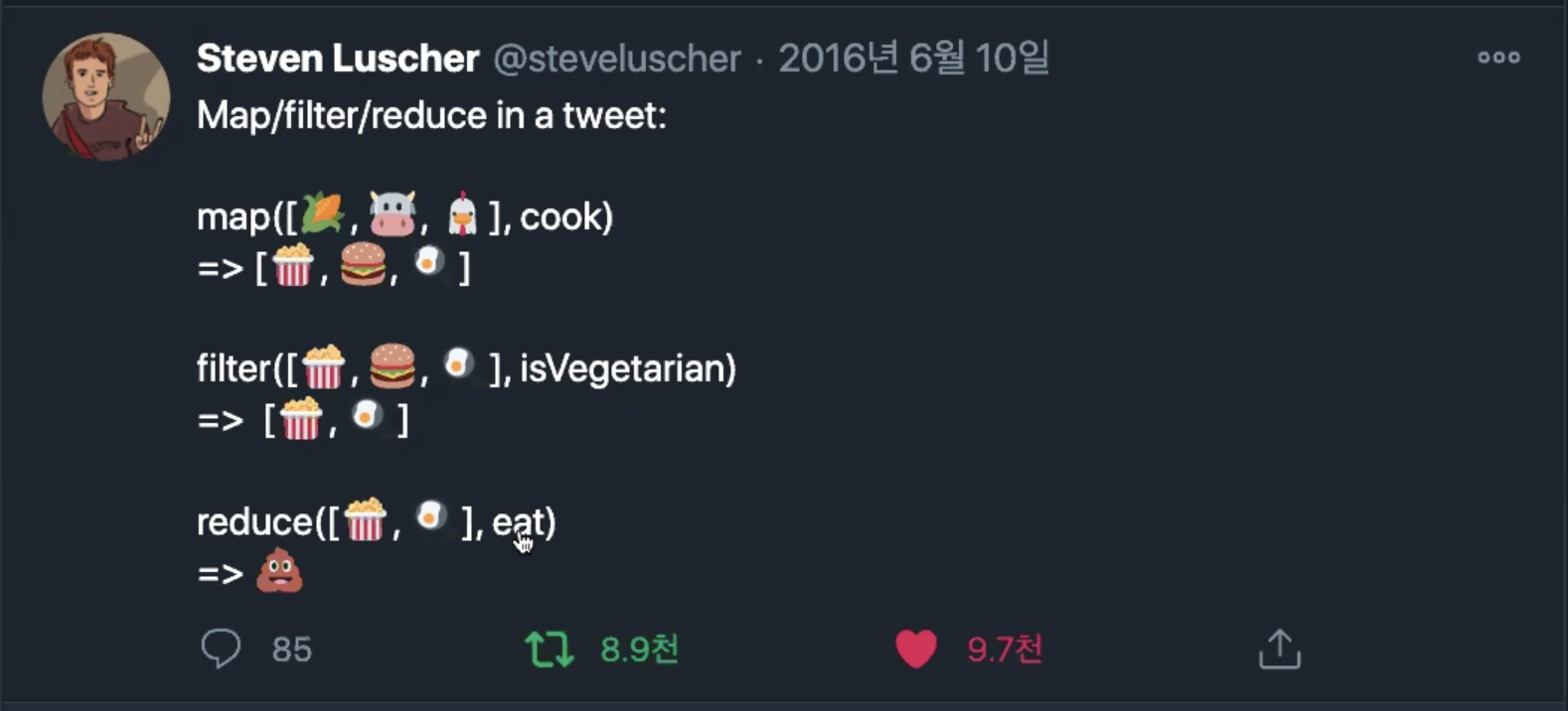
- Array.prototype.filter() 분류해서 거르기!!
- filter out with elements that satisfy certain condition from array
- condition has to be delivered in function form as an argument of filter method
- part of higher order function since function takes as an argument
- returns back as an 'ARRAY' to callback function that takes argument
- 'CALLBACK' function will return a Boolean value
- If result is 'TRUE', it will create an array with that element, if not, NO
-
1234567891011function getIndex(arr, num) {return arr.filter(function (el) {return el < num;}).length; // make an array with true value and get the length of that array}function filterOddLengthWords(words) {return words.filter(function (word) {return word.length % 2 !== 0; // create an array that is true});}
cs
- Array.prototype.map() 대응, 갯수를 맞춰줘야 됨 배열자체의 수정용!!
- creates a 'NEW ARRAY' populated with result of calling a provided function on every element in the calling array
- can extract values from list of objects
12345function getOnlyNames(arr) {return arr.map(function (el){return el.name; // extract value of name through map filter})}
cs
- Array.protoype.reduce() 변환이 되어 응축, 연산용!!
- executes a reducer function(that you provide) on each element of the array, resulting in 'SINGLE OUTPUT VALUE'
- can make various type
- arr.reduce(callback[, initialValue])
- 초기값 설정 중요!
- if they want empty array, put [] like this
- if there is initial value, it becomes first value to calculate(A value to use as the first argument to the first call of the callback. If no initialValue is supplied, the first element in the array will be used as the initial accumulator value and skipped as currentValue.)
12345function computeProductOfAllElements(arr) {return arr.reduce(function(acc, cur){return acc * cur}, 1) //1 is initial value}
cs
- 초기값 설정 중요!
- use when you want to merge arrays by using concat
-
12345function joinArrayOfArrays(arr){return arr.reduce(function(acc, cur){return acc.concat(cur)})}
cs
-
- If array is empty and there is no initial value, it will return 'typeerror'
- If array is empty and there is inital value, it will return initial value
- Array.prototype.sort()
- sorts the elements of an array in place and returns the 'SORTED ARRAY'
- default sort order is ascending, built upon converting elements into string then comparing their sequences of UTF-16 code units values
- a[key] > b[key]=> a-b=positive(3-1=2)
- if it is true, return 1 which makes A to go to back
- a[key] < b[key] => a-b=negative(1-3=-2)
- if it is true, return -1, which makes B to go to back
- a[key] = b[key]
- return 0, leave as it is
12345678910items.sort(function (a, b) {if (a.value > b.value) {return 1;}if (a.value < b.value) {return -1;}// a must be equal to breturn 0;});
cs
- return 0, leave as it is
- Array.prototype.some()
- tests whether 'AT LEAST ONE ELEMENT' in the array 'PASSES' the test implemented by the provided function
- returns a Boolean Value
- Array.prototype.every()
- tests whether 'ALL ELEMENTS' in the array 'PASS' the test implemented by the provided function
- returns a Boolean value
- Array.prototype.forEach()
- executes a provided function 'ONCE FOR EACH ARRAY ELEMENT'
- Array.prototype.find()
- returns the value of the 'FIRST ELEMENT' in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function
'TIL' 카테고리의 다른 글
| TIL 2020.11.12 (0) | 2020.11.14 |
|---|---|
| TIL 2020.11.11 (0) | 2020.11.14 |
| TIL 2020.11.08 (0) | 2020.11.08 |
| TIL 2020.11.07 (0) | 2020.11.07 |
| TIL 2020.11.06 (0) | 2020.11.06 |